
Project: Streamlit App for Rainfall prediction
Posted in :
🌧️ Rainfall Prediction App – Will it rain tomorrow in Australia?
In this project, I built a Streamlit-based interactive web application that predicts whether it will rain tomorrow in Australia. The model behind this app is trained on 10 years of historical weather observation data from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) using a Random Forest Classifier.

📋 Table of Content
- Overview
- Key Features
- Technical Details & Technologies
- Getting Started
- Dataset
- Model Development
- Examples & Visualizations
- Challenges & Learnings
- Future Improvements
🌟 Overview
This app helps users decide whether to carry an umbrella by predicting the likelihood of rainfall for the next day. It leverages 10 years of daily weather data across Australian cities, preprocesses and visualizes the data, and uses a Random Forest classification model for prediction.
✅ Key Features
- 🔍 Interactive data exploration and preprocessing visualizations
- 🧠 Machine learning model trained with resampling and hyperparameter tuning
- ⚖️ Handles imbalanced data through upsampling
- 🔢 One-hot encoding and outlier capping for clean, robust feature sets
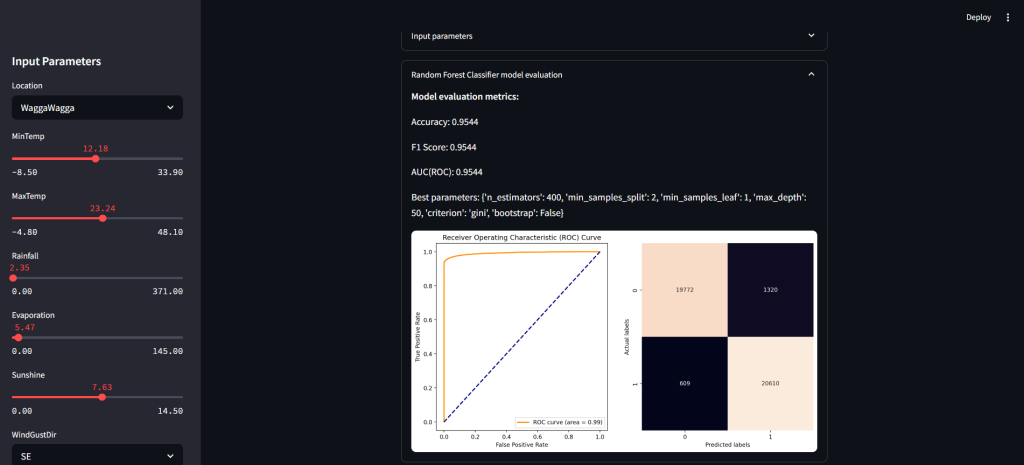
- 📈 Model evaluation with ROC curve, confusion matrix, and metrics
- 📊 Streamlit sidebar for live user input and instant predictions
🛠️ Technical Details & Technologies
- Language: Python 3.8+
- Framework: Streamlit
- Machine Learning: scikit-learn
- Data Handling: Pandas, NumPy
- Visualization: Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly
- Model: Random Forest Classifier with RandomizedSearchCV for tuning
- Other Tools: OneHotEncoder, StandardScaler
🚀 Getting Started
Prerequisites
- Python 3.8+
- pip or conda
- Streamlit installed (pip install streamlit)
Installation
git clone https://github.com/your-username/rainfall-prediction-app.git
cd rainfall-prediction-app
pip install -r requirements.txtRun the app
streamlit run app.py📊 Dataset
- Source: BOM weatherAUS dataset
- Size: ~145,000 rows × 23 columns
- Period: 2008–2017
- Target Variable: RainTomorrow (Yes / No)
- Features: Temperature, humidity, pressure, wind speed, and others
- Missing Values: Handled via location-wise imputation (mean/mode)
🤖 Model Development
🔍 Preprocessing
- Dropped irrelevant columns like Date
- Imputed missing values by location using mean/mode
- One-hot encoding for categorical variables
- Capped outliers at 25th and 75th percentiles
- Upsampled minority class (RainTomorrow=Yes)
🧠 Model
- Algorithm: Random Forest Classifier
- Training: Train/Test split + 8-fold Stratified Cross-Validation
- Hyperparameter Tuning: RandomizedSearchCV
- Scaling: StandardScaler applied to numerical features
📏 Evaluation Metrics
- Accuracy: ~0.9416
- F1 Score: ~0.9415
- ROC AUC: ~0.9415
- Includes ROC Curve and Confusion Matrix
📸 Examples & Visualizations
- Correlation heatmaps
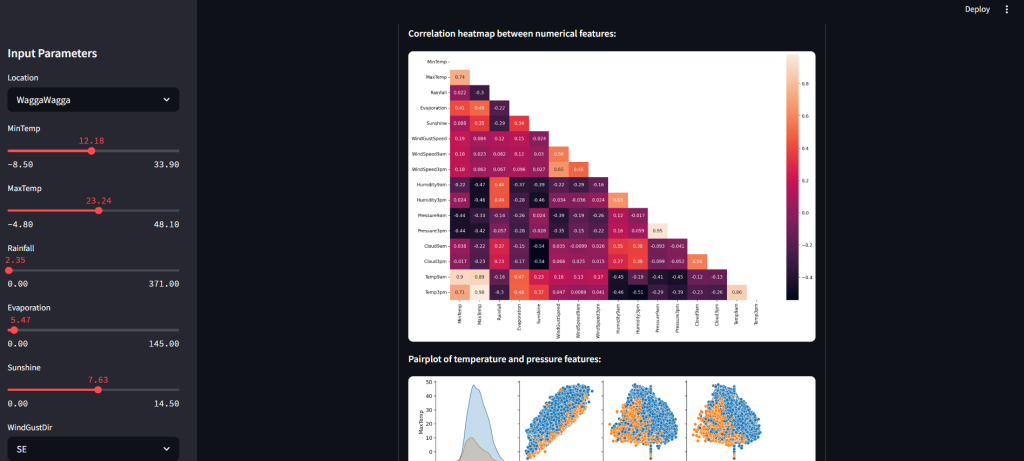
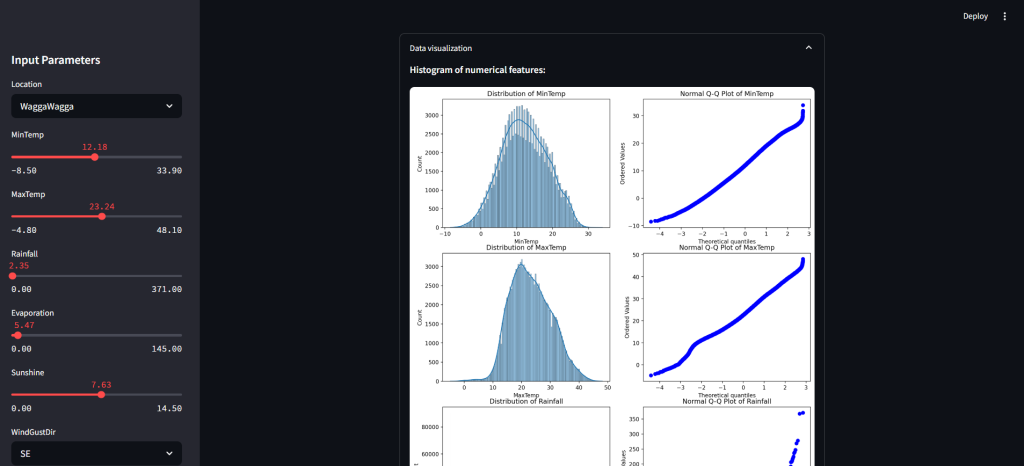
- Feature distributions and data range summaries
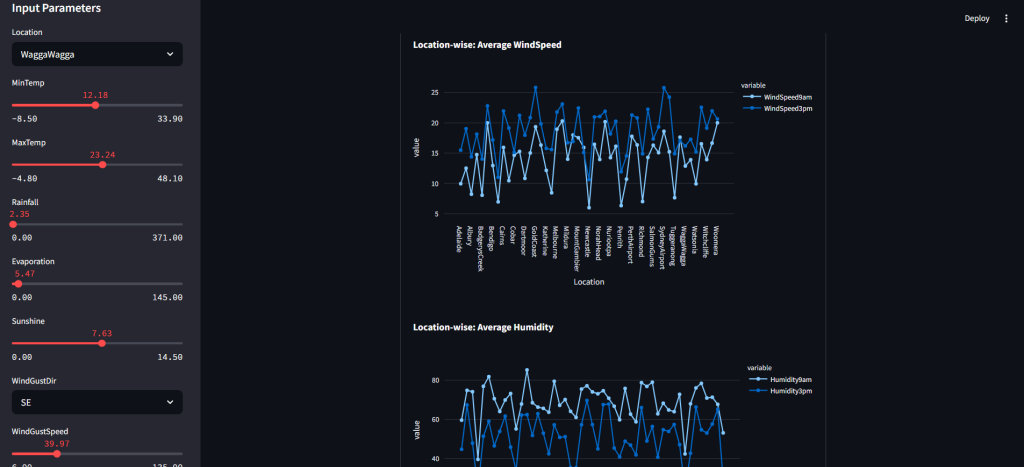
- Location-wise trends in temperature, humidity, and pressure
- ROC curve and confusion matrix for model performance
Sample prediction output:
“It will not rain tomorrow 🌞, with a probability of 82%”
🧠 Challenges & Learnings
- Handling missing data by group-level imputation improved model generalization
- Dealing with class imbalance significantly improved model fairness
- Encoding and scaling had to be aligned precisely between training and inference pipelines
- Learned how to design user-friendly ML dashboards using Streamlit
🚧 Future Improvements
- Deploy the app publicly (Streamlit Cloud, Hugging Face Spaces, or Heroku)
- Improve mobile responsiveness and UI polish
- Add SHAP/LIME model explainability tools
- Compare with other models (e.g., XGBoost, LightGBM, neural networks)
- Serialize model pipeline using joblib for efficient reloading